This post is intended for those with React and RxJS experience. I’m just sharing patterns I found useful while making this UI.
Here’s what we’re building:
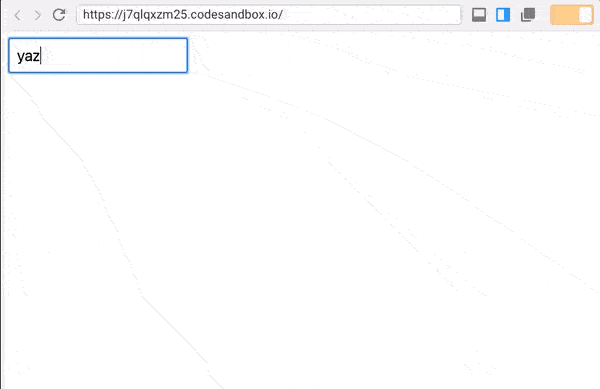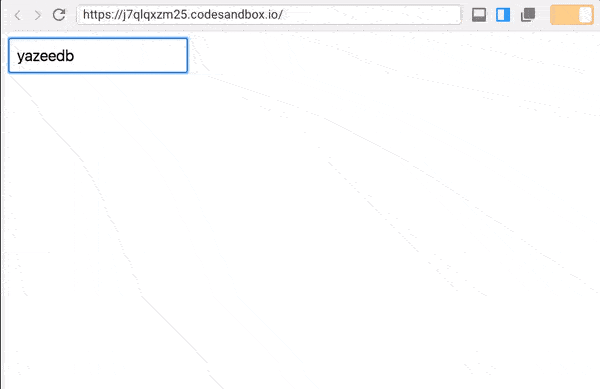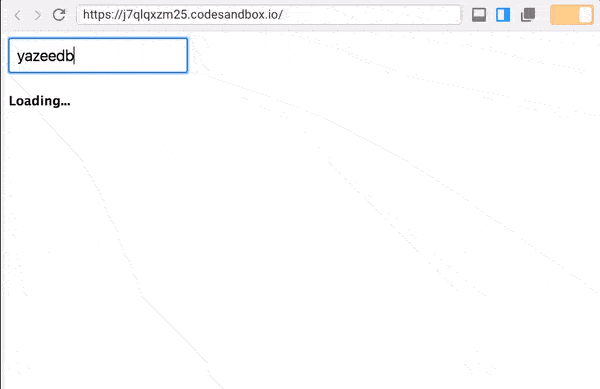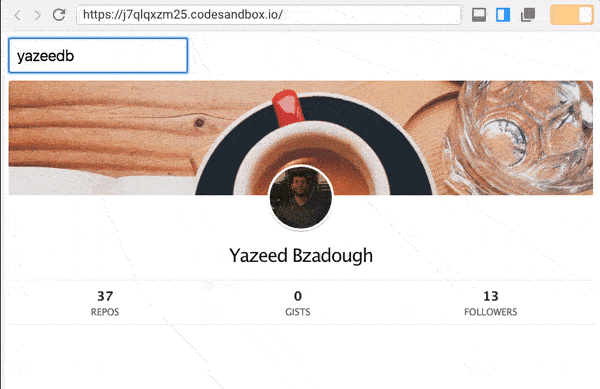
No classes, lifecycle hooks, or setState.
Setup
Everything’s on my GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/yazeedb/recompose-github-ui
cd recompose-github-ui
yarn installThe master branch has the finished project, so checkout the start branch if you wish to follow along.
git checkout start
And run the project.
npm start
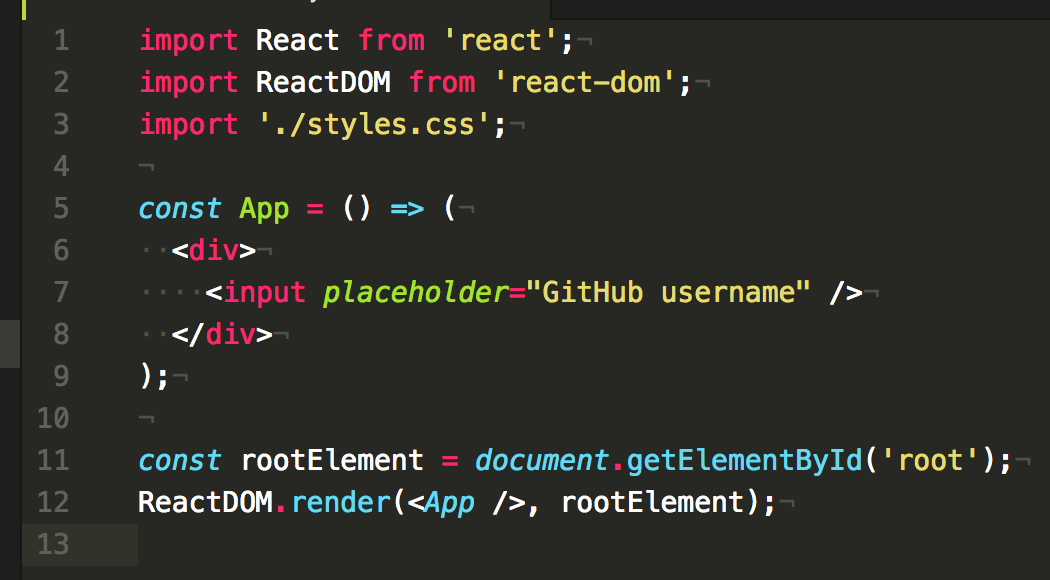
The app should be running on localhost:3000, and here’s our initial UI.

Open the project in your favorite text editor and view src/index.js.
Recompose
If you haven’t seen it yet, Recompose is a wonderful React utility belt for making components in a functional programming style. It has a ton of functions, and I’d have a hard time picking my favorites.
It’s Lodash/Ramda, but for React. I also love that they support observables. Quoting from the docs:
It turns out that much of the React Component API can be expressed in terms of observables
We’ll be exercising that concept today! 😁
Streaming Our Component
Right now App is an ordinary React component. We can return it through an observable using Recompose’s componentFromStream function.
This function initially renders a null component, and re-renders when our observable returns a new value.
A Dash of Config
Recompose streams follow the ECMAScript Observable Proposal. It lays out how observables should work when they eventually ship to modern browsers.
Until they’re fully implemented, however, we rely on libraries like RxJS, xstream, most, Flyd, and so on.
Recompose doesn’t know which library we’re using, so it provides a setObservableConfig to convert ES Observables to/from whatever we need.
Create a new file in src called observableConfig.js.
And add this code to make Recompose compatible with RxJS 6:
import { from } from 'rxjs';
import { setObservableConfig } from 'recompose';
setObservableConfig({
fromESObservable: from
});Import it into index.js:
import './observableConfig';And we’re ready!
Recompose + RxJS
Import componentFromStream.
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { componentFromStream } from 'recompose';
import './styles.css';
import './observableConfig';And begin redefining App with this code:
const App = componentFromStream((prop$) => {
// ...
});Notice that componentFromStream takes a callback function expecting a prop$ stream. The idea is that our props become an observable, and we map them to a React component.
And if you’ve used RxJS, you know the perfect operator to map values.
Map
As the name implies, you’re transforming Observable(something) into Observable(somethingElse). In our case, Observable(props) into Observable(component).
Import the map operator:
import { map } from 'rxjs/operators';And redefine App:
const App = componentFromStream((prop$) => {
return prop$.pipe(
map(() => (
<div>
<input placeholder="GitHub username" />
</div>
))
);
});Ever since RxJS 5, we use pipe instead of chaining operators.
Save and check your UI, same result!
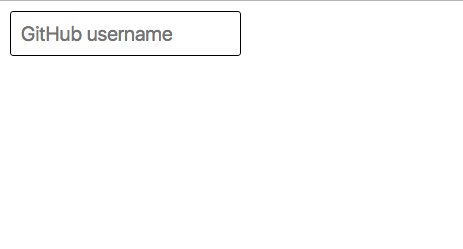
Adding an Event Handler
Now we’ll make our input a bit more reactive.
Import the createEventHandler from Recompose.
import { componentFromStream, createEventHandler } from 'recompose';And use it like so:
const App = componentFromStream((prop$) => {
const { handler, stream } = createEventHandler();
return prop$.pipe(
map(() => (
<div>
<input onChange={handler} placeholder="GitHub username" />{' '}
</div>
))
);
});createEventHandler is an object with two interesting properties: handler and stream.
Under the hood, handler is an event emitter pushing values to stream, which is an observable broadcasting those values to its subscribers.
So we’ll combine the stream observable and the prop$ observable to access the input’s current value.
combineLatest is a good choice here.
Chicken and Egg Problem
To use combineLatest, though, both stream and prop$ must emit. stream won’t emit until prop$ emits, and vice versa.
We can fix that by giving stream an initial value.
Import RxJS’s startWith operator:
import { map, startWith } from 'rxjs/operators';And create a new variable to capture the modified stream.
const { handler, stream } = createEventHandler();
const value$ = stream.pipe(
map((e) => e.target.value),
startWith('')
);We know that stream will emit events from input’s onChange, so let’s immediately map each event to its text value.
On top of that, we’ll initialize value$ as an empty string — an appropriate default for an empty input.
Combining It All
We’re ready to combine these two streams and import combineLatest as a creation method, not as an operator.
import { combineLatest } from 'rxjs';You can also import the tap operator to inspect values as they come:
import { map, startWith, tap } from 'rxjs/operators';And use it like so:
const App = componentFromStream((prop$) => {
const { handler, stream } = createEventHandler();
const value$ = stream.pipe(
map((e) => e.target.value),
startWith('')
);
return combineLatest(prop$, value$).pipe(
tap(console.warn),
map(() => (
<div>
<input onChange={handler} placeholder="GitHub username" />
</div>
))
);
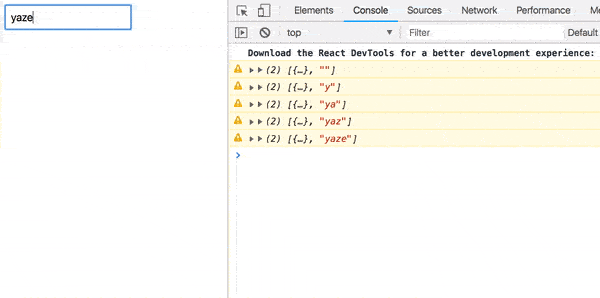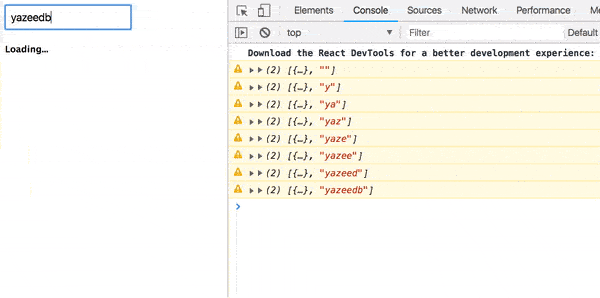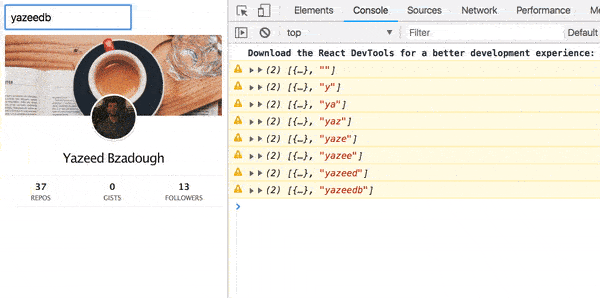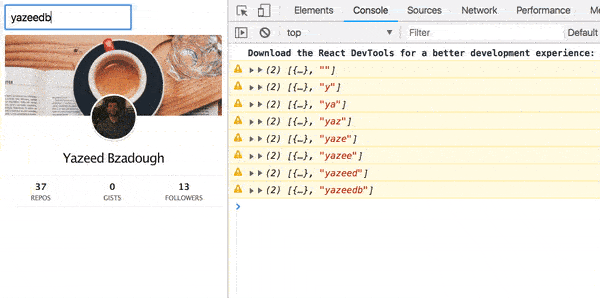
});Now as you type, [props, value] is logged.
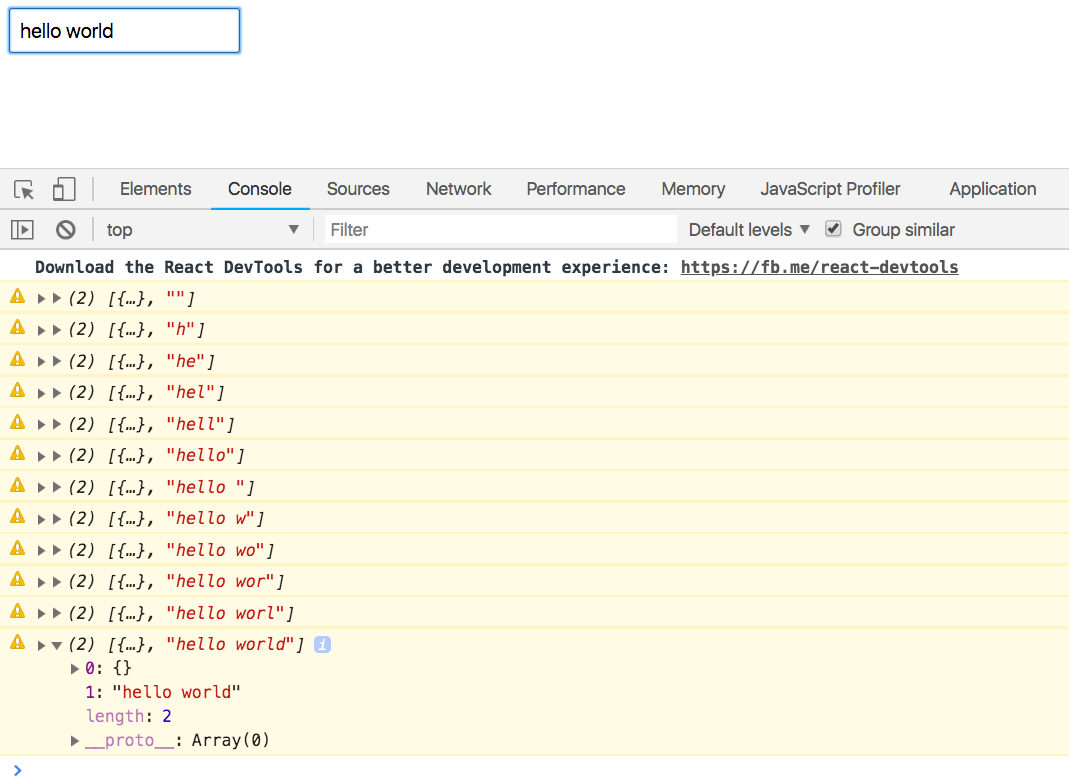
User Component
This component will be responsible for fetching/displaying the username we give it. It’ll receive the value from App and map it to an AJAX call.
JSX/CSS
It’s all based off this awesome GitHub Cards project. Most of the stuff, especially the styles, is copy/pasted or reworked to fit with React and props.
Create a folder src/User, and put this code into User.css:
And this code into src/User/Component.js:
The component just fills out a template with GitHub API’s standard JSON response.
The Container
Now that the “dumb” component’s out of the way, let’s do the “smart” component:
Here’s src/User/index.js:
import React from 'react';
import { componentFromStream } from 'recompose';
import { debounceTime, filter, map, pluck } from 'rxjs/operators';
import Component from './Component';
import './User.css';
const User = componentFromStream((prop$) => {
const getUser$ = prop$.pipe(
debounceTime(1000),
pluck('user'),
filter((user) => user && user.length),
map((user) => <h3>{user}</h3>)
);
return getUser$;
});
export default User;We define User as a componentFromStream, which returns a prop$ stream that maps to an <h3>.
debounceTime
Since User will receive its props through the keyboard, we don’t want to listen to every single emission.
When the user begins typing, debounceTime(1000) skips all emissions for 1 second. This pattern’s commonly employed in type-aheads.
pluck
This component expects prop.user at some point. pluck grabs user, so we don’t need to destructure our props every time.
filter
Ensures that user exists and isn’t an empty string.
map
For now, just put user inside an <h3> tag.
Hooking It Up
Back in src/index.js, import the User component:
import User from './User';
And provide value as the user prop:
return combineLatest(prop$, value$).pipe(
tap(console.warn),
map(([props, value]) => (
<div>
<input onChange={handler} placeholder="GitHub username" />
<User user={value} />{' '}
</div>
))
);Now your value’s rendered to the screen after 1 second.
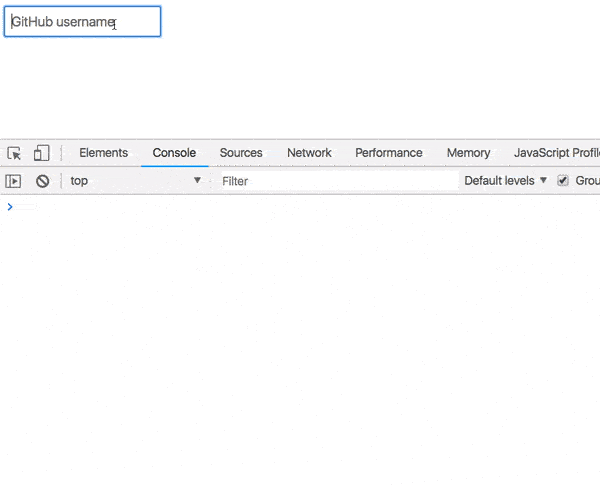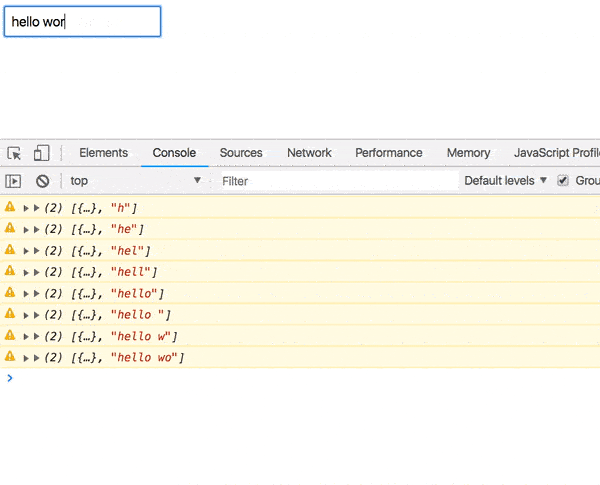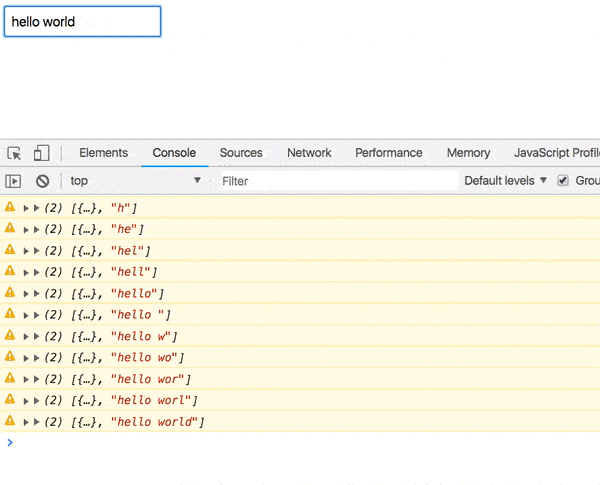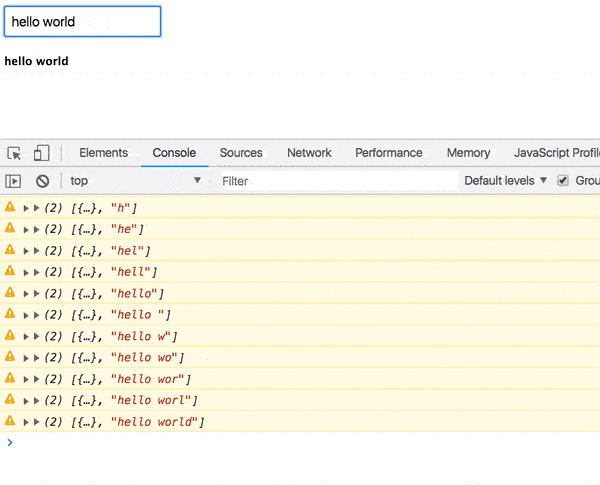
Good start, but we need to actually fetch the user.
Fetching the User
GitHub’s User API is available here. We can easily extract that into a helper function inside User/index.js:
const formatUrl = (user) => `https://api.github.com/users/${user}`;Now we can add map(formatUrl) after filter:
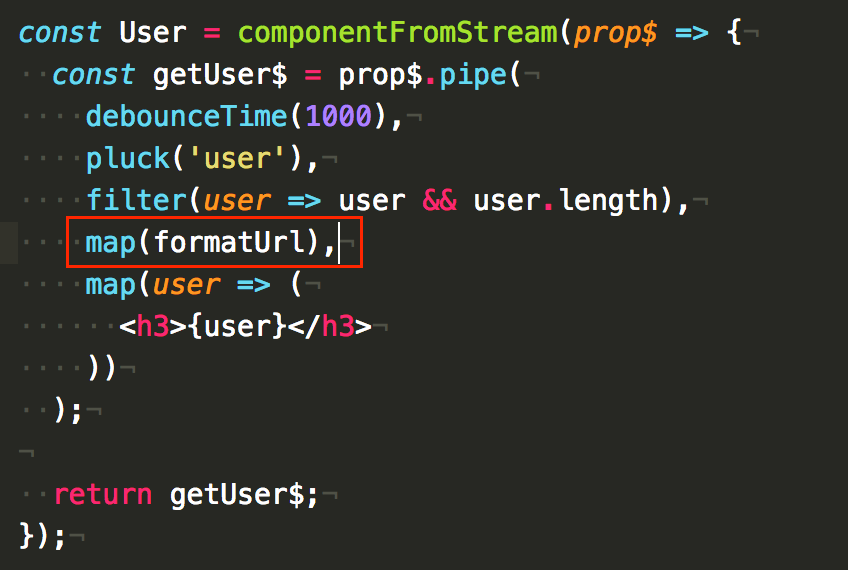
You’ll notice the API endpoint is rendered to the screen after 1 second now:
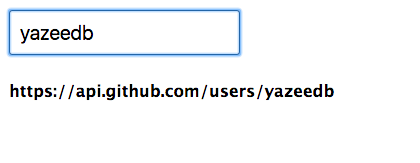
But we need to make an API request! Here comes switchMap and ajax.
switchMap
Also used in type-aheads, switchMap’s great for literally switching from one observable to another.
Let’s say the user enters a username, and we fetch it inside switchMap.
What happens if the user enters something new before the result comes back? Do we care about the previous API response?
Nope.
switchMap will cancel that previous fetch and focus on the current one.
ajax
RxJS provides its own implementation of ajax that works great with switchMap!
Using Them
Let’s import both. My code is looking like this:
import { ajax } from 'rxjs/ajax';
import { debounceTime, filter, map, pluck, switchMap } from 'rxjs/operators';And use them like so:
const User = componentFromStream((prop$) => {
const getUser$ = prop$.pipe(
debounceTime(1000),
pluck('user'),
filter((user) => user && user.length),
map(formatUrl),
switchMap((url) =>
ajax(url).pipe(
pluck('response'),
map(Component)
)
)
);
return getUser$;
});Switch from our input stream to an ajax request stream. Once the request completes, grab its response and map to our User component.
We’ve got a result!
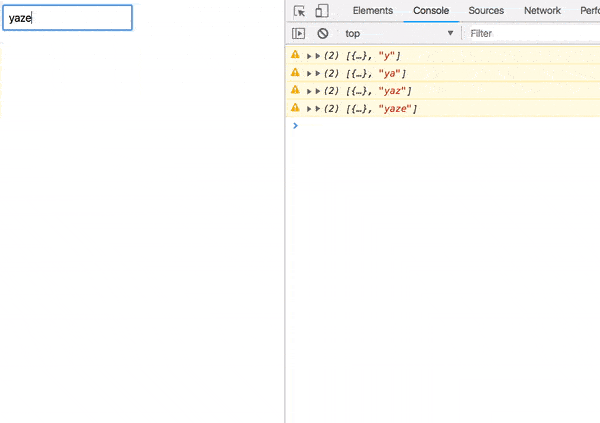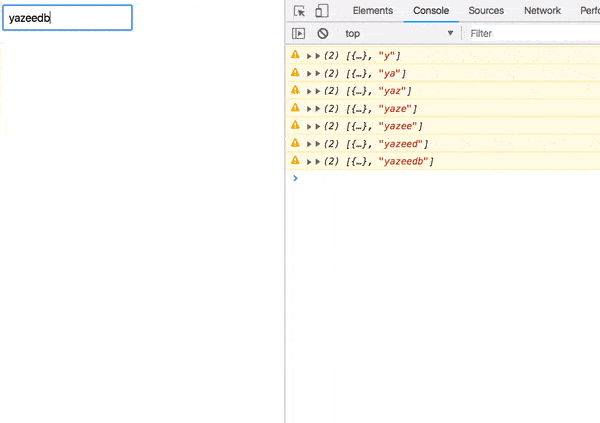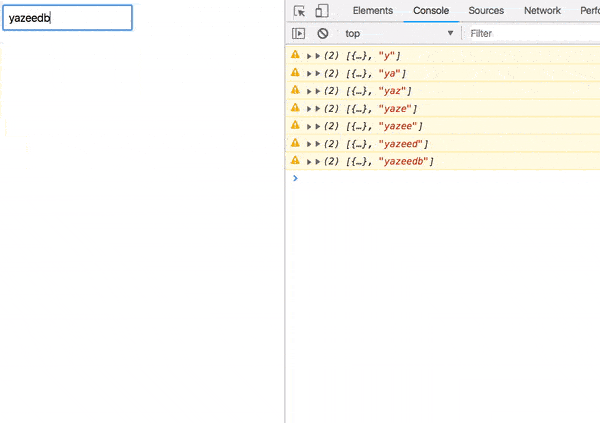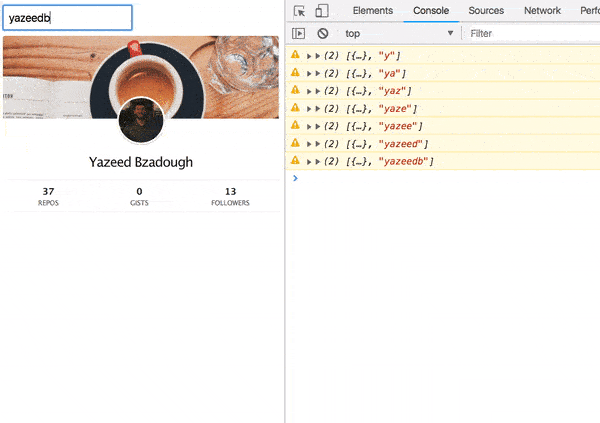
Error handling
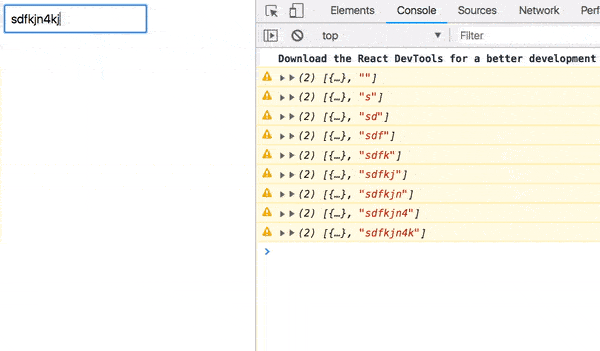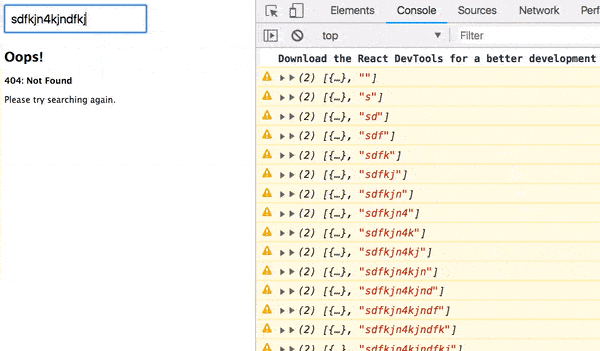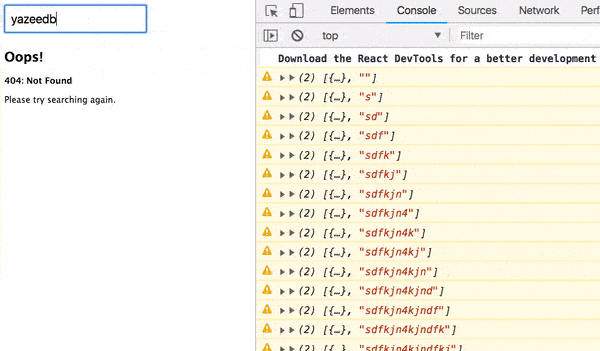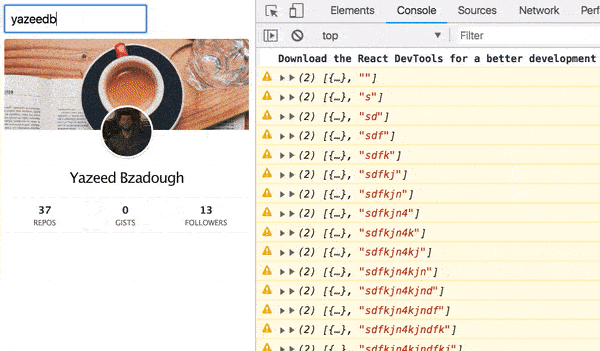
Try entering a username that doesn’t exist.
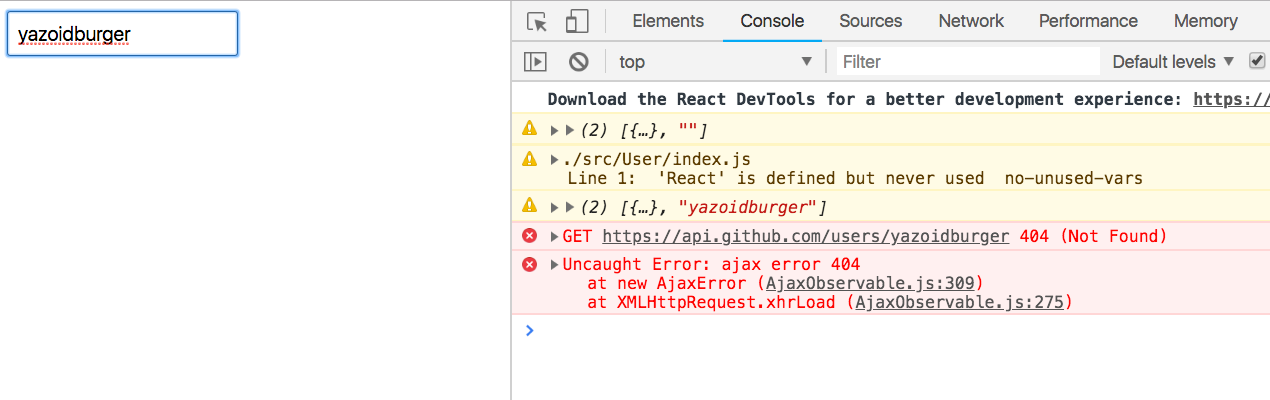
Even if you change it, our app’s broken. You must refresh to fetch more users.
That’s a bad user experience, right?
catchError
With the catchError operator, we can render a reasonable response to the screen instead of silently breaking.
Import it:
import {
catchError,
debounceTime,
filter,
map,
pluck,
switchMap
} from 'rxjs/operators';And stick it to the end of your ajax chain.
switchMap((url) =>
ajax(url).pipe(
pluck('response'),
map(Component),
catchError(({ response }) => alert(response.message))
)
);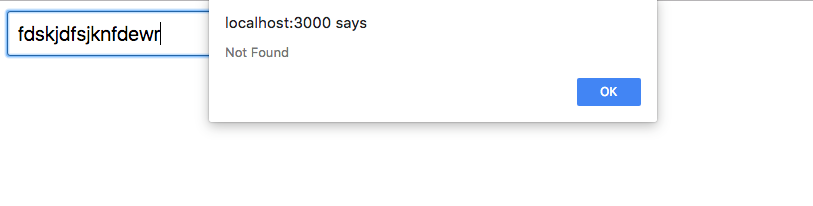
At least we get some feedback, but we can do better.
An Error Component
Create a new component, src/Error/index.js.
import React from 'react';
const Error = ({ response, status }) => (
<div className="error">
<h2>Oops!</h2>
<b>
{status}: {response.message}
</b>
<p>Please try searching again.</p>
</div>
);
export default Error;This will nicely display response and status from our AJAX call.
Let’s import it in User/index.js:
import Error from '../Error';And of from RxJS:
import { of } from 'rxjs';Remember, our componentFromStream callback must return an observable. We can achieve that with of.
Here’s the new code:
ajax(url).pipe(
pluck('response'),
map(Component),
catchError((error) => of(<Error {...error} />))
);Simply spread the error object as props on our component.
Now if we check our UI:
Much better!
A Loading Indicator
Normally, we’d now require some form of state management. How else does one build a loading indicator?
But before reaching for setState, let’s see if RxJS can help us out.
The Recompose docs got me thinking in this direction:
Instead of
setState(), combine multiple streams together.
Edit: I initially used BehaviorSubjects, but Matti Lankinen responded with a brilliant way to simplify this code. Thank you Matti!
Import the merge operator.
import { merge, of } from 'rxjs';When the request is made, we’ll merge our ajax with a Loading Component stream.
Inside componentFromStream:
const User = componentFromStream((prop$) => {
const loading$ = of(<h3>Loading...</h3>);
// ...
});A simple h3 loading indicator turned into an observable! And use it like so:
const loading$ = of(<h3>Loading...</h3>);
const getUser$ = prop$.pipe(
debounceTime(1000),
pluck('user'),
filter((user) => user && user.length),
map(formatUrl),
switchMap((url) =>
merge(
loading$,
ajax(url).pipe(
pluck('response'),
map(Component),
catchError((error) => of(<Error {...error} />))
)
)
)
);I love how concise this is. Upon entering switchMap, merge the loading$ and ajax observables.
Since loading$ is a static value, it’ll emit first. Once the asynchronous ajax finishes, however, it’ll emit and be displayed on the screen.
Before testing it out, we can import the delay operator so the transition doesn’t happen too fast.
import {
catchError,
debounceTime,
delay,
filter,
map,
pluck,
switchMap,
tap
} from 'rxjs/operators';And use it just before map(Component):
ajax(url).pipe(
pluck('response'),
delay(1500),
map(Component),
catchError((error) => of(<Error {...error} />))
);Our result?
I’m wondering how far to take this pattern and in what direction. Please share your thoughts!